Case Studies
The evaluation of fPMC was carried out using three different software systems and processes, which were taken from the related literature (i.e., FX system, PL system, and COM process).
Descriptions of each case study are provided below, preceded by a summary of their characteristics. Our analysis of the research papers published in leading software engineering venues between 2016-2020 indicates that the types of PCTL formulae supported by fPMC are representative of typical software engineering projects.
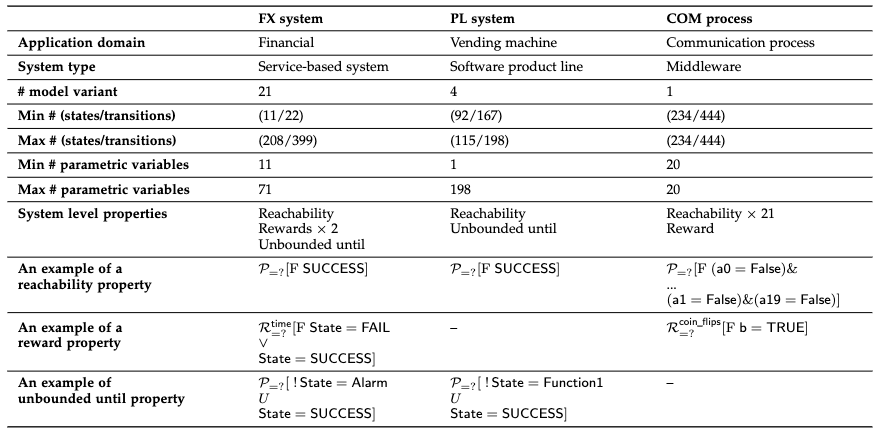
Summary of three software systems and processes used in the paper
FX System
Overview
The FX model has two execution modes that a trader can choose from: an expert mode and a normal mode. In the expert mode, the Market watch operation extracts real-time exchange rates (bid/ask price) of selected currency pairs, and this information is then passed to the Technical analysis operation for further analysis, such as evaluating the current trading conditions, predicting future price movement, and deciding which actions to take. There are three actions can be taken: 1) carrying out a trade by calling the Order operation; 2) continuously performing the Market watch; and 3) reporting an error and triggering the Alarm. In the normal mode, the system uses Fundamental analysis operation to evaluate the economic outlook of a country and decides whether to 1) call the Order operation to trade the currency, 2) re-do the Fundamental analysis operation; or 3) exit the program.
We analysed four non-functional properties of the FX system as:
- Reachability (P1) The probability of successful completion;
- Reachability reward (P2) The expected execution time;
- Unbounded until (P3) The probability of successful completion without triggering the alarm;
- Reachability reward (P4) The expected cost;
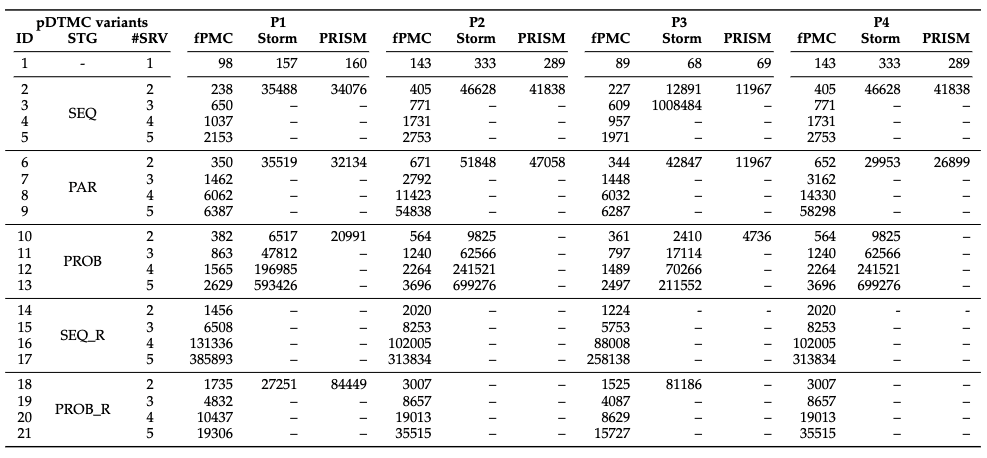
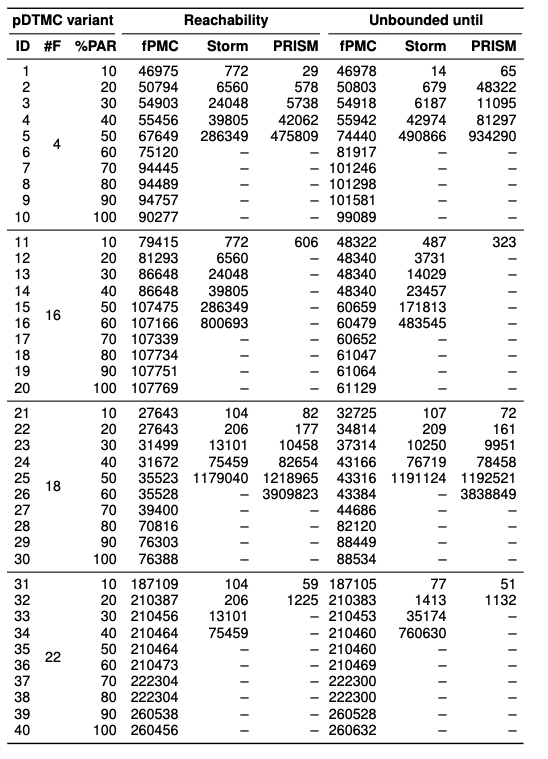
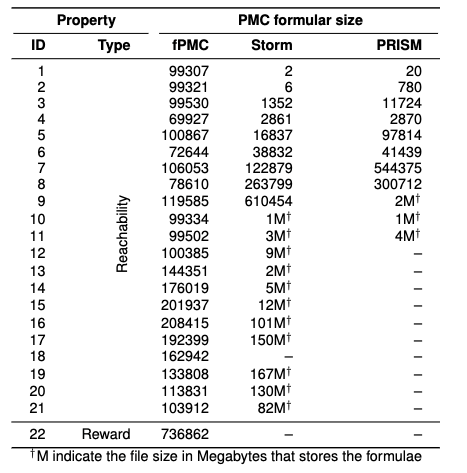
The table below shows the number of arithmetic operations in the derived algebraic formulae.
fPMC repository, models and properties for the FX system
| File | Description |
|---|---|
| Models and properties | ZIP file containing 21 pDTMC models (specified in PRISM language) and 4 non-functional properties (specified in PCTL) |
| Repository of fPMC generated results | ZIP file containing the modelling pattern resturned by performing fPMC, which includes pDTMCs and properties for all fragments and the abstract model |
PL System
Overview
The PL system models the process in various vending machines that enable a user to insert coins and select a beverage. The features of this system comprise the beverage type (soda, tea, or both), payment mode (cash or free) and taste preference (e.g., add lemon, sugar), enabling the derivation of vending machines, and accordingly defining pDTMCs, whose structures contain between 4 and 22 features.
We analysed two non-functional properties of the PL system as:
- Reachability The probability of successful completion;
- Unbounded until The probability of successful completion without adding sugar in the drink.
The table below shows the number of arithmetic operations in the derived algebraic formulae.
fPMC repository, models and properties for PL system
| File | Description |
|---|---|
| Models and properties | ZIP file containing 44 parametric DTMC model variants (specified in PRISM language) and 2 non-functional properties (specified in PCTL) |
| Repository of fPMC generated results | ZIP file containing the modelling pattern returned by performing fPMC, which includes pDTMCs and properties for all fragments and the abstract model |
COM Process
Overview
COM process is a communication process among n identical individuals, inspired by how honeybees emit an alarm pheromone to recruit workers and protect their colonies from intruders. Due to the self- destructive defence behaviour in social insects, the recruited workers die after completing their defence actions. Hence, a balance between efficient defence and preservation of a critical worker's mass can be found. The induced pDTMC is a stochastic population model with n parameters.
We analysed two non-functional properties of the COM process as:
- Reachability The probability of successful communication (×21);
- Reachability reward The expect cost of communication (×1).
The table below shows the number of arithmetic operations in the derived algebraic formulae.
fPMC repository, models and properties for PL system
| File | Description |
|---|---|
| Models and properties | ZIP file containing 1 parametric DTMC model (specified in PRISM language) and 22 non-functional properties (specified in PCTL) |
| Repository of fPMC generated results | ZIP file containing the modelling pattern returned by performing fPMC, which includes pDTMCs and properties for all fragments and the abstract model |
Analysing impact of 𝞪
The figure below shows the impact of 𝞪 across all three software systems and processes in terms of execution time and the size of derived formulae
(a),(b) and (c) differentiate pDTMCs used in the experiment, and they were from FX system, PL system and COM system respectively. Time(a), Time(b) and Time(c) show time in seconds that fPMC successfully obtains the algebra expression of a pDTMC with different α value used. The (#OP(a),#OP(b) and #OP(c)) show the number of operations(#OP) in the obtained algebra expressions. For each plot, the total Time or total #OP are also decomposed in details as those are associated with fragments and the abstract model respectively
fPMC repository for analysing impact of α
| File | Description |
|---|---|
| Repository of fPMC generated results | ZIP file containing the modelling pattern returned by performing fPMC (used for plotting the figure), which includes pDTMCs and properties for all fragments and the abstract model |